The Economic Times, Nov 23, 2018
View: India’s socio-political narrative has changed to BJP’s advantage
By Nilanjan Mukhopadhyay
Recently, there were two eye witnesses to an attempted burglary: a neighbourhood Muslim tailor, and a Hindu watchman. Both saw burglars arrive on motorcycles and get away after their failed attempt. The police scanned CCTV footage at a neighbour’s residence and, on zeroing in on some suspects, summoned the tailor and guard for identification.
The owner of the house where the police were at, reluctantly permitted the Muslim tailor inside, telling the police, “You never know them. He may see the footage and get ideas.” Later, an elderly lady in the neighbourhood enquired if the suspects seen on the CCTV footage video ‘looked Muslim’.
Cowering in Fear
In most parts of India, there is nothing unusual about such exchanges. Underprivileged Muslims are welcome to better-off, predominantly Hindu localities for work. But there is a threshold they must not cross. At the end of each day, they return to their ghettos, and are watched more intensely by the police than the colonies where disadvantaged Hindus live.
Some Muslim families do live — disproportionately — in middle-class and upwardly mobile colonies. Social interactions with Hindus are restricted and, barring odd instances, few have close friends from the other community. Prejudice towards minorities, chiefly Muslims, is not a recent phenomenon. Divisions have existed since ages, in many cases heightened after Partition, especially among the traumatised. But being unapologetically suspicious of Muslims is relatively new, the earlier hypocritical, more shrouded form being increasingly disposed of.
It would be tempting to lay the blame for such a development solely on the BJP’s and its affiliates’ doorstep. This is a simplistic way of comprehending a complex phenomenon. Yes, there are reasons for accusing elements of the party of polarisation since the Ram Janmabhoomi agitation in the late 1980s. Yet, one would be an ostrich by pretending that the phenomenon of distrust becoming legitimate sentiment, is solely the result of BJP’s pursuits.
Over the last few years, there has been a paradigm shift in socio-political discourse across the spectrum. The post-Independence consensus — that minorities, especially Muslims, must be made to feel at ease in a secular India —has significantly weakened. No societal contract — as opposed to the constitutional one — can be gauged any more on the ‘responsibility’ of the majority to create an atmosphere in which India’s Muslims are assured that their ancestors took the correct decision to not migrate to Pakistan.
Future historians would be better placed to flag the point when this shift took place. Today, one can only surmise that the change is as much the result of BJP’s propagation of Hindutva, as it is the acceptance of this framework by other parties, ‘secular’ ones included. From a time when BJP’s adversaries contested this framework ideologically, they now vie with it as its ‘true’ flagbearers.
Take the stance over faith as determinant in the Ayodhya dispute. Initial attempts to have it proved that the temple town was indeed Rama’s birthplace was abandoned, and replaced with the construct that matters of faith need not be proved and are not judiciable. In the ongoing assembly polls, Congress has actually pledged support for constructing the Ram Path Gaman, the mythical pathway Ram is believed to have traversed during his vanvaas.
Since September 2017, Congress president Rahul Gandhi has regularly visited temples during polls — to correct the impression that, in Sonia Gandhi’s ‘infamous’ words, Congress was ‘prominority’. From when identifying with those on the margins of society was politically correct — and correct politically — being on the right side of majoritarian thinking is now viewed as practical.
Till the Cows Come Home
Globally, there is rising support for illiberalism and sectarianism. At a recent dialogue with visiting German journalists in New Delhi, the conversation dwelled significantly on similarities and dissimilarities between Hindu nationalistic thought and ideas that have propelled the Alternative for Germany (AfD) emerging as the third-largest group in the Bundestag. Even in the US, the wave of Islamophobia is echoed in certain Indian debates on issues like cow protection and illegal immigrants far more than they were immediately after 9/11or even 26/11.
India has undergone at least two phases, when almost every political party adopted positions around a central political idea. After Independence, much of the public discourse centred around the Nehruvian economic model and socialism that existed in various shades: Nehruvian, Lohiate, communist and even a Jan Sangh variety.
Later, secularism became the focal point with BJP, too, claiming to practise the ‘genuine’ secularism while labelling its opponents as ‘pseudo-secularists’.
Now, most leaders across the political spectrum are willing to display their ‘Hinduness’, or ‘being Hindu’. After Prime Minister Narendra Modi had turned down an offer to wear a skull cap in public, Bihar chief minister Nitish Kumar had famously said how in India ‘one has to wear the topi at times, and on other occasions, sport a tilak’. Today, wearing the topi has probably become optional.
This is not about ritual practise, but how a nation is imagined and the space of minorities within it. Even a BJP defeat in state elections, or even the Lok Sabha elections, is unlikely to restore the previous template. Battlelines have been drawn within the ‘Hindutva’ terrain.
Some have soft postures, others hard. But the thought-processor of the India Machine will be this, at least for some time to come.
skip to main |
skip to sidebar

Communalism all day everyday (hk 2015)


extract from a photo on street

Seeds of Hate - Picture of Bricks collected by the Hindu right Ram Janmabhoomi movement (Photo PTI)
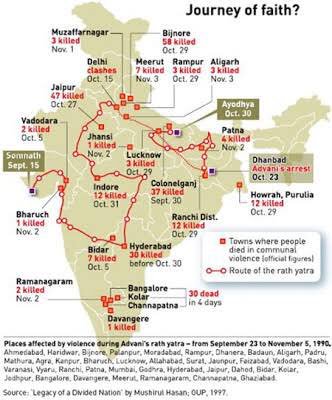
Journey of Faith? - Places affected by violence during BJP's Rath Yatra
Resources for all concerned with culture of authoritarianism in society, banalisation of communalism, (also chauvinism, parochialism and identity politics) rise of the far right in India (and with occasional information on other countries of South Asia and beyond)
Subscribe via email
see Comunalism Watch on mobile phones
Archive
Links
- Fast Track To Troubling Times: 100 Days of Narendra Modi – A Counter Report
- Hindu Nationalism in the United States: A Report on Nonprofit Groups
- Gujarat Carnage 2001-2010
- Communalism Combat
- Anhad
- Sahmat News
- Plural India
- Citizens For Justice and Peace
- Coalition Against Communalism
- For Defence of Teesta Setalvad
- Secular Democracy
- Citizens For Peace
- South Asia Citizens Web
- Truth of Gujarat
- Desh Kosh
- Feku
- Vision Jafri
- Narendra Modi Facts
- Orissa Burning: The anti christian pogrom of Aug-Sep 2008
- Remembering 1992
- Thus Spake Srikrishna
- Janta Ka Aina
- Onlinevolunteers org
- Campaign to Stop Funding Hate
- Awaaz South Asia
- Coalition Against Genocide
- Sangh Samachar
- Stop The Hatred
- Barbarta Kay Virudh: An anti fascist blog in Hindi
- The Pink Chaddi Campaign
- Ban Vishwa Hindu Parishad
- Report of Indian People's Tribunal on Communalism in Orissa
- The Truth on Gujarat 2002 - A Tehelka investigation
- Communalism and Religious Fundamentalism in India: A Resource File [A PDF file]
- Secularism is a women's issue
- Centre for Secular Space
- Human Rights for All
- Gulail
- Holy Cow & Other Bull
- Searchlight Magazine
- Anti Fascist Network
- Ras l'front
Pages
Tags / Keywords
Translate
Feed from Dilip Simeon's blog
Communalism all day everyday

Communalism all day everyday (hk 2015)
See Therapist for "Hurt Sentiments"
Freedom from Hindutva
extract from a photo on street

Seeds of Hate - Picture of Bricks collected by the Hindu right Ram Janmabhoomi movement (Photo PTI)
Map of L K Advani's Rath Yatra of 1990

Journey of Faith? - Places affected by violence during BJP's Rath Yatra
About Us / Disclaimer
This is a collaborative space run by an informal collective of people from across India and elsewhere. The blog was started many years ago under the aegis of South Asia Citizens Web. All web content placed here is done in public interest; it may be freely used by people for non commercial purposes. Please remember to give credit to original copyrighted sources and seek permission for further use.
Disclaimer: Posting of content here does not constitute endorsement by the Communalism Watch Cooperative.
Disclaimer: Posting of content here does not constitute endorsement by the Communalism Watch Cooperative.