Economic Times - October 7, 2015
Beef politics: Food-Poisoning India
By Saba Naqvi
The bloodletting over beef that ‘may or may not have been beef ’ has exposed the historical fault-line that runs across India. Our attention has been focused on the Hindi heartland, the cow belt, where the nastiest contemporary mobilisations have taken place. There are consequences elsewhere.
The Hindi heartland has a history of cow agitations. In 1882, Dayananda Saraswati, founder of the Arya Samaj, began a movement demanding the end of cow slaughter under the British Raj. One of the first recorded riots over cow took place in Mau in Azamgarh in 1893.
But independent India had, by and large, found a balance on this tricky issue, by banning cow slaughter in most northern parts of the country even as buffalo meat became our ‘beef ’, the ambiguity keeping the delicate ‘Indian tapestry’ intact.
With the murder of Mohammed Akhlaq in Dadri, UP, last Monday, rabid groups now riding on a majoritarian tide have ripped apart that weave. To enter the kitchens of fellow Indians and thrash or kill them for what they eat is a serious threat to the sanity that holds our republic together. A new ecosystem is being put into place. Bans imposed by states only legitimises the existence of groups we call ‘the fringe’.
The serious political consequences of the Dadri murder are also being felt in a part of India that is tenuously linked to the rest of the country. In Kashmir last week, I was repeatedly confronted with the argument that the Two-Nation Theory — religion, as opposed to ethnicity or language, is the unifying force for Muslims in the Indian subcontinent — propounded by Mohammad Ali Jinnah was being resurrected.
Despite the creation of Bangladesh and ethnic wars in Pakistan, the Two-Nation Theory is now a sort of emblematic slogan for groups in Kashmir whenever they feel overwhelmed by ‘India’. In other words, when our secularism looks hollow, so do our arguments in Kashmir.
Untitled-1
Arecent Jammu court order enforcing an old ban on the sale of beef in the state — where the traditional meat is mutton — had sparked protests. Mercifully, on October 5, the Supreme Court suspended the order for two months. Still, the lynching of Akhlaq has reinforced the ‘Pakistan constituency’ in the Valley.
Even if we put aside humanism and see the events unfolding through the prism of nationalism, they diminish India when the trends in our country are compared to those that have systematically made Pakistan afailed state. The world took note when a young Christian couple was lynched 40 km from Lahore in November 2014 on the unproven charge of blasphemy. The lynching of a Muslim in Dadri on the outskirts of Delhi, too, has not gone unnoticed.
Imanaged my own little conflagration this Eid near my home in Mehrauli, near the Qutub Minar. There is asmall madrasa near my house next to a temple. On Eid day, it was surrounded by police and I saw a truck loaded with cattle. I imagined that the police had stopped the traditional Qurbani and confiscated the animals.
The next morning I learnt that the windshields of 20 cars parked on the main road had been smashed and that “the Muslims have done it”. I visited the madrasa where the boys were in a huddle. The maulana said that they traditionally performed the Eid sacrifice for people in the locality. This year, there were complaints, so they themselves had asked the police to take the livestock to another designated spot.
Could the boys have smashed the cars in anger? The maulana ruled out the possibility since they could not have left the area with the police surrounding the madrasa through Eid. The police verified this version and believed that outside miscreants were behind the cars being damaged.
More than a week later, the police are still guarding the madrasa.
The police have kept the peace and done the right thing. The maulana, too, did the right thing by sending away the animals designated for sacrifice. But he is now worried that the local residents’ welfare association (RWA), with its eye on the land, wants the madrasa gone.
I also learnt that the temple next to the madrasa has no water supply. So, the madrasa provides it a supply line from its borewell. The maulana and the pujari have differences, but they can also be friends. It’s a tenuous peace. But it’s a peace that must be kept.
(For a counterview, read Scroll’s ‘Indian Muslims are living at the mercy of Hindus’ at goo.gl/CVgY9Y)
skip to main |
skip to sidebar

Communalism all day everyday (hk 2015)


extract from a photo on street

Seeds of Hate - Picture of Bricks collected by the Hindu right Ram Janmabhoomi movement (Photo PTI)
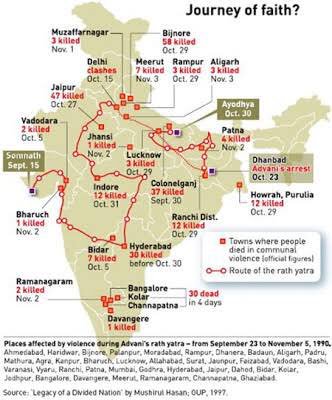
Journey of Faith? - Places affected by violence during BJP's Rath Yatra
Resources for all concerned with culture of authoritarianism in society, banalisation of communalism, (also chauvinism, parochialism and identity politics) rise of the far right in India (and with occasional information on other countries of South Asia and beyond)
Subscribe via email
see Comunalism Watch on mobile phones
Archive
Links
- Fast Track To Troubling Times: 100 Days of Narendra Modi – A Counter Report
- Hindu Nationalism in the United States: A Report on Nonprofit Groups
- Gujarat Carnage 2001-2010
- Communalism Combat
- Anhad
- Sahmat News
- Plural India
- Citizens For Justice and Peace
- Coalition Against Communalism
- For Defence of Teesta Setalvad
- Secular Democracy
- Citizens For Peace
- South Asia Citizens Web
- Truth of Gujarat
- Desh Kosh
- Feku
- Vision Jafri
- Narendra Modi Facts
- Orissa Burning: The anti christian pogrom of Aug-Sep 2008
- Remembering 1992
- Thus Spake Srikrishna
- Janta Ka Aina
- Onlinevolunteers org
- Campaign to Stop Funding Hate
- Awaaz South Asia
- Coalition Against Genocide
- Sangh Samachar
- Stop The Hatred
- Barbarta Kay Virudh: An anti fascist blog in Hindi
- The Pink Chaddi Campaign
- Ban Vishwa Hindu Parishad
- Report of Indian People's Tribunal on Communalism in Orissa
- The Truth on Gujarat 2002 - A Tehelka investigation
- Communalism and Religious Fundamentalism in India: A Resource File [A PDF file]
- Secularism is a women's issue
- Centre for Secular Space
- Human Rights for All
- Gulail
- Holy Cow & Other Bull
- Searchlight Magazine
- Anti Fascist Network
- Ras l'front
Pages
Tags / Keywords
Translate
Feed from Dilip Simeon's blog
Communalism all day everyday

Communalism all day everyday (hk 2015)
See Therapist for "Hurt Sentiments"
Freedom from Hindutva
extract from a photo on street

Seeds of Hate - Picture of Bricks collected by the Hindu right Ram Janmabhoomi movement (Photo PTI)
Map of L K Advani's Rath Yatra of 1990

Journey of Faith? - Places affected by violence during BJP's Rath Yatra
About Us / Disclaimer
This is a collaborative space run by an informal collective of people from across India and elsewhere. The blog was started many years ago under the aegis of South Asia Citizens Web. All web content placed here is done in public interest; it may be freely used by people for non commercial purposes. Please remember to give credit to original copyrighted sources and seek permission for further use.
Disclaimer: Posting of content here does not constitute endorsement by the Communalism Watch Cooperative.
Disclaimer: Posting of content here does not constitute endorsement by the Communalism Watch Cooperative.