The Times of India
Gujarat 2002 vs Delhi 1984: Which genocide should we vote against?
Anahita Mukherji
14 September 2013, 04:57 PM IST
The two most widely reported news stories on Friday the 13th, 2013, have a lesson in store for the country. The men who raped and brutalised a young girl in a moving bus in Delhi last year have been awarded the death sentence. The man who oversaw one of independent India’s worst instances of communal violence, in which thousands of women were raped and tortured, has been given the chance to become India’s next prime minister. And the party he wishes to defeat has gone largely unpunished for another dastardly act of communal violence.
Some skeletons refuse to remain locked in a closet, no matter how firmly we shut the door. The ghosts of Sikhs roasted alive in Delhi 30 years ago, and Muslims gang-raped and chopped into pieces over a decade ago in Gujarat have come back to haunt India’s two largest national parties in the run up to the 2014 elections.
For many young Indians — the census suggests that much of India is young — the bloodbath in Gujarat is a distant memory and most were not born when Sikhs were slaughtered in Delhi. But in the last one year, both massacres have clawed their way back into public memory. A BJP minister from Gujarat was sentenced to life imprisonment for her role in the 2002 violence, and court cases against two Congress leaders have resurfaced in connection with the 1984 massacre.
Both Gujarat 2002 and Delhi 1984 have often been dismissed as spontaneous riots. There is much to suggest they were neither spontaneous, nor riots, but systematic acts of ethnic cleansing targeting two of India’s minority communities.
Recent debates focus on the impact of both pogroms on the upcoming Lok Sabha elections. But can we reduce crimes against humanity to an election campaign? Is that all that genocide means to us? How do we decide which genocide to vote for and which to vote against? Is there any foot-ruler or weighing scale that can help us measure two acts of barbarism to figure out which one is worse?
Or maybe we could use the response to the Delhi gang rape as a benchmark for how justice should be sought. We did not compare the Delhi rape case to other rape cases in order to judge the extent of brutality committed. We did not say that, since many rape victims have been denied justice, we should deny this young girl justice too.
So why should we pit Gujarat 2002 against Delhi 1984? Can we not, as a nation, use the 2014 elections to demand justice for both genocides?
Much has been said on the need to move over the massacres, and focus, instead on “the development plank” which refers, among other things, to building roads, highways and efficient transport. But can the denial of justice for genocide be substituted with good roads? Is that the price of human life? If so, how many dead bodies are equal to one good road?
No country that I am aware of has successfully moved on from genocide without dealing with the ghosts of the past. Germany did not overcome its Nazi legacy by forgetting the pogrom against Jews. Instead, it witnessed the Nuremberg Trials, where some of the most prominent members of Hitler’s Third Reich were brought to book. There is a Holocaust Memorial in Berlin, and Nazi concentration camps such as Auschwitz in Poland have been turned into museums. The streets of Germany are strews with Stolperstein (German for stumbling block), cobblestone sized memorials for Holocaust victims.
Post-apartheid South Africa set up a Truth and Reconciliation Commission, headed by Archbishop Desmond Tutu, with the aim of promoting “reconciliation and forgiveness among the perpetrators and victims of apartheid by the full disclosure of the truth.”
Neither country moved over community violence by forgetting about it and building roads instead. Its time India, too, remembered its dead and looked both massacres straight in the eye.
It’s time we revisited the story of Kausar Bano, a pregnant young woman in Gujarat, whose stomach was slashed open, foetus torn out and burnt alive.
Women in Gujarat weren’t simply raped, they were also mutilated, burnt, chopped into pieces and had hard objects inserted inside them. While analysing the “special savagery” with which wombs and vaginas were attacked in Gujarat, Tanika Sarkar writes in the Economic and Political Weekly of how rape is seen as a sign of collective dishonouring in community violence. Mobs in Gujarat were dressed in khakhi shorts and saffron underwear, with rape viewed as a religious duty.
The targeted violence against Muslims and Sikhs was as symbolic as it was grotesque. The manner in which Sikhs had their hair torn off before being dismembered showed the simultaneous defiling of one’s body and religion.
William Dalrymple writes of “hair, piles of hair, cut from Sikhs before they were burnt alive.” Every journalist who has covered the massacre of Sikhs in Delhi’s Trilokpuri colony talks of having to tread with care while walking the streets for fear of stepping on human entrails and hacked off limbs. Little wonder then, that senior journalist Khushwant Singh, who sought refuge in the house of a Swedish diplomat at the time, told a commission probing the violence that he had felt like a Jew in Nazi Germany, a refugee in his homeland, all because he was Sikh.
Many Sikhs removed their turbans and cut their hair to survive the pogrom. Gurmej Singh was not one of them. His turban marked him out on a train from Punjab to Bombay, which stopped at a station near Delhi the day Indira Gandhi was assassinated. His widow, Mohinder Kaur, fights back tears on a BBC documentary as she recalls the armed men who jumped onto the train, beat her husband with iron rods, dragged him out and set him on fire.
Both massacres involved the cynical use of religion. Both used similar rhetoric. The butchering of Muslims in Gujarat was seen as a way to teach a community a lesson for the burning of a train in Godhra, while the killing of Sikhs was viewed as punishment for the assassination of a Prime Minister by her Sikh bodyguards.
In both instances, the entire state machinery worked against the victims of violence, while shielding the perpetrators. Many have spoken of the military precision with which the violence took place.
“No riot can continue beyond a few hours without the active connivance of the local police and magistracy,” writes Harsh Mander, social worker and member of India’s National Advisory Council, on the violence in Gujarat.
Both the BJP and Congress have been accused of crimes of omission and commission.
An eye-witness-turned-hostile in the anti-Sikh pogrom, said in his first affidavit that he saw Congress politician Jagdish Tytler lead a mob which set fire to a Gurdwara and burnt a man alive.
While Congress leader Sajjan Kumar was acquitted in one of three cases against him in the anti-Sikh violence, the CBI had earlier talked of a “conspiracy of terrifying proportion with the complicity of police and patronage of local MP Sajjan Kumar.”
Mayaben Kodnani former minister of woman and child development in Gujarat — was awarded a life sentence for her role in the massacre of nearly 100 people in Naroda Patia, the same massacre where Kausar Banu’s stomach was ripped and foetus torn out. Eyewitnesses say Kodnani led a raging mob to attack the Muslim area, fired a shot from a pistol and distributed weapons. One witness in the case was hacked to death in 2011.
The Narendra Modi-led BJP government in Gujarat distanced itself from Kodnani after the conviction. But could Gujarat’s BJP leadership have been completely clueless about her role in the violence, when, in 2007, she was promoted to minister for woman and child development?
The Supreme Court appointed Special Investigative Team’s claim that the violence in Gujarat was spontaneous has been hotly contested. Investigative journalist Ashish Khetan showed that the Gujarat government ignored early warnings of crowds being mobilised and the possibility of riots.
An election year is a great time to press for justice for both genocides. Those among us who have grown weary and cynical of elections in India might want to seek inspiration from Egypt, a nascent democracy emerging from an era of dictatorship, with far fewer electoral options than India, which voted with its feet against Hosni Mubarak, a secular, neo-liberal dictator, and then took to the streets against the Muslim Brotherhood which replaced him.
My piece is not about which party one should vote for or against in the 2014. Voting for one or another national party, or any other party for that matter, is a personal choice. My point is simple. Can’t we, the people of a nation with far more evolved legal mechanisms than the struggling democracies of the middle-East, use a national election to demand the justice for genocide?
skip to main |
skip to sidebar

Communalism all day everyday (hk 2015)


extract from a photo on street

Seeds of Hate - Picture of Bricks collected by the Hindu right Ram Janmabhoomi movement (Photo PTI)
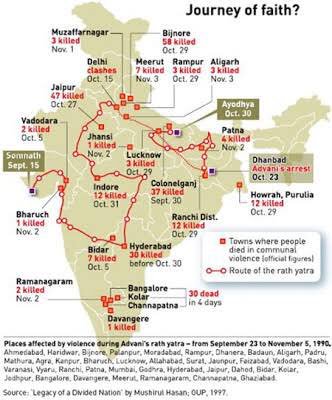
Journey of Faith? - Places affected by violence during BJP's Rath Yatra
Resources for all concerned with culture of authoritarianism in society, banalisation of communalism, (also chauvinism, parochialism and identity politics) rise of the far right in India (and with occasional information on other countries of South Asia and beyond)
Subscribe via email
see Comunalism Watch on mobile phones
Archive
Links
- Fast Track To Troubling Times: 100 Days of Narendra Modi – A Counter Report
- Hindu Nationalism in the United States: A Report on Nonprofit Groups
- Gujarat Carnage 2001-2010
- Communalism Combat
- Anhad
- Sahmat News
- Plural India
- Citizens For Justice and Peace
- Coalition Against Communalism
- For Defence of Teesta Setalvad
- Secular Democracy
- Citizens For Peace
- South Asia Citizens Web
- Truth of Gujarat
- Desh Kosh
- Feku
- Vision Jafri
- Narendra Modi Facts
- Orissa Burning: The anti christian pogrom of Aug-Sep 2008
- Remembering 1992
- Thus Spake Srikrishna
- Janta Ka Aina
- Onlinevolunteers org
- Campaign to Stop Funding Hate
- Awaaz South Asia
- Coalition Against Genocide
- Sangh Samachar
- Stop The Hatred
- Barbarta Kay Virudh: An anti fascist blog in Hindi
- The Pink Chaddi Campaign
- Ban Vishwa Hindu Parishad
- Report of Indian People's Tribunal on Communalism in Orissa
- The Truth on Gujarat 2002 - A Tehelka investigation
- Communalism and Religious Fundamentalism in India: A Resource File [A PDF file]
- Secularism is a women's issue
- Centre for Secular Space
- Human Rights for All
- Gulail
- Holy Cow & Other Bull
- Searchlight Magazine
- Anti Fascist Network
- Ras l'front
Pages
Tags / Keywords
Translate
Feed from Dilip Simeon's blog
Communalism all day everyday

Communalism all day everyday (hk 2015)
See Therapist for "Hurt Sentiments"
Freedom from Hindutva
extract from a photo on street

Seeds of Hate - Picture of Bricks collected by the Hindu right Ram Janmabhoomi movement (Photo PTI)
Map of L K Advani's Rath Yatra of 1990

Journey of Faith? - Places affected by violence during BJP's Rath Yatra
About Us / Disclaimer
This is a collaborative space run by an informal collective of people from across India and elsewhere. The blog was started many years ago under the aegis of South Asia Citizens Web. All web content placed here is done in public interest; it may be freely used by people for non commercial purposes. Please remember to give credit to original copyrighted sources and seek permission for further use.
Disclaimer: Posting of content here does not constitute endorsement by the Communalism Watch Cooperative.
Disclaimer: Posting of content here does not constitute endorsement by the Communalism Watch Cooperative.