From Outlook Magazine, Magazine | Mar 05, 2012
gujarat riots
A Beast Asleep?
Ten years after Gujarat 2002, Outlook asks if we’re likely to witness such horror again
by Saba Naqvi , Smruti Koppikar
India is a nation that was born in the bloodshed and displacement of the Partition riots. In its DNA, it inherited the schizoid gene of being a large Hindu nation with one of the world’s largest Muslim populations. It was a historical faultline that was exploited for politics time and again. Ahimsa was the Gandhian ideal we paid lip service to but the reality far too often was mass violence. In urban ghettos, in the old cities across the land, small riots were part of the cycle of life. A religious procession would be taken out, a skirmish would take place, curfew would be clamped, a minor riot would have just taken place or been barely averted.
But the Gujarat riots of 2002 marked the apogee of communal hatred. Ten years after the Sabarmati Express coach was set afire in Godhra on February 27, and after the bloodbath that followed, we must pause and ask: can it happen again? Many would argue that it cannot because, in the long term, Narendra Modi has had to pay a price for presiding over a bloodbath after the advent of 24-hour television. In the immediate aftermath of the riots, however, he gained enormously. Modi ran a communally charged election campaign six months after the violence, when he would famously use “Mian Musharraf” as a rhetorical term for the entire Muslim community. Modi had been sent to Gujarat in October 2001, at a time when the BJP under Keshubhai Patel was doing badly and had lost a byelection. He began his first term as CM on Oct 7, 2001; five months later, the carnage happened; later in the year, in December 2002, he won the state election with a huge margin and began his second term. He has now been the longest-serving chief minister of Gujarat and will contest later this year for a fourth term.
Bombay 1992-93 Babri demolition sparks off first phase in Dec. A rampaging Sena fans flames through incendiary articles and inciting attacks on Muslim localities. (Photograph by Sherwin Crasto)
He most famously used communal polarisation as a political technique and it worked within the boundaries of Gujarat. Sociologist Ashis Nandy says that the problem also arose because for “months afterwards, Modi celebrated the riots. He appeared to be showing off”. Even the Shiv Sena, which had a decade before Gujarat orchestrated vicious riots in Mumbai, looked like relative amateurs at the riot technique compared to the systematic method that was applied and revelled in inside Gujarat. Nandy points out that the anti-Sikh riots of 1984 actually claimed the largest toll. But it’s a blot the Congress always tries to live down and not celebrate. “The whole psychology was different as Sikhs were a prosperous community that people admired and envied,” says Nandy. The Hindu-Muslim equation is another story.
As for Modi, he has become the development man, the business-friendly leader, but his image makeover as an acceptable national figure has not worked. Even BJP president Nitin Gadkari says, “What happened in Gujarat was an unfortunate incident. I don’t think it can or should happen again.”
“I don’t think it can happen again, not because of any growth in ethics but because the political costs of riots have been rising since 1984 and after 2002, Narendra Modi has blown any chance of ever being PM.” Ashis Nandy, Sociologist “Riots are regular occurrences at low levels of national income. With rising incomes, communal discontent does not fully disappear, but it begins to take the form of hi-tech terrorism as opposed to low-tech mass riots.” Ashutosh Varshney, Author and academic
“The possibility of a big riot happening cannot be ruled out. We cannot forget that there is no preventive law in place and those guilty of orchestrating riots are not punished. But we have faith in majority, civil society and the media.” Mahmood Madani, MP and cleric “Aggressive Gujarati middle class believes in hard Hindutva; elsewhere middle class at best believes in soft Hindutva. The only place I can see it being replicated is Karnataka but the middle class there is more diverse.” Achyut Yagnik, Author and historian
“A Gujarat-type riot can happen only if there’s complicity between the Centre and state government. Which is what happened in ’02. The Sangh has not given up on that kind of mobilisation; they are trying it in Karnataka.” B.K. Hari Prasad, Congress leader “1992-93 won’t happen in the same way in the near future because the potential of that particular anti-minority track has been temporarily exhausted. Majority and minority communities have become more self- reflexive.” Kamala Ganesh, Sociologist
“There was a context to riots and places where riots were habitual. Today there are different concerns, the human rights industry has emerged, media is more intrusive; consequently administrations have to be more responsive.” Swapan Dasgupta,
Right-wing ideologue “Mumbai is even today a tinderbox and vested interests can still play with
people’s emotions. The scale of violence may be difficult but not impossible because people who order such riots sit safe somewhere and stand to gain.” Julio F. Ribeiro, Ex-police chief, Mumbai
“There were always political motives to the riots in Hyderabad. Sometimes Bajrang Dal, sometimes MIM, sometimes the Andhra lobby. Now things have changed because of the media and Hyderabad’s expansion.” Amir Ali Khan, Siasat, Hyderabad “No riot can happen without tension being built up by parties and outfits. Average citizens and party workers react out of insecurity, not animosity. That insecurity not only still exists in Mumbai, at times it’s even sharper.” Asghar Ali Engineer, Islamic scholar
“Riots can happen again in Mumbai.
The rhetoric against north Indians is similar and we have also seen sporadic violent attacks against bhaiyyas although Mumbai moves on our finance and enterprise.” Sanjay Nirupam, Congress MP “The poorer people of Mumbai have moved northwards which means fewer paradoxes exist. The spoils of power and office are now distributed among the parties, which means all shades of politicians are busy getting wealthy.” Aroon Tikekar, Historian
Modi is stuck with the taint because Gujarat was the first mega riot in the age of 24-hour TV. There were victims in Mumbai, Surat, Bhagalpur, Jamshedpur, Hyderabad, Moradabad, Bhiwandi, earlier riots in Ahmedabad, a city that actually recorded one of the first big post-Partition riots in 1969. But they were just numbers, death tolls, the faceless victims of communal carnage.
But in Gujarat 2002, the stories were documented in heart-wrenching detail and etched in our collective memories. How Bilqis Bano’s daughter was snatched from her hands, flung against a rock, killed, and the pregnant woman raped repeatedly; how Zahira Sheikh survived the grisly burning of the Best Bakery in which her family was roasted alive; how limbs of children were hacked and little boys flung to their death in Naroda Patiya; how Ehsaan Jafri begged for the life of those who had sought his protection in Gulberg Society; how his widow Zakia Jafri still fights for justice and says her husband called the CM’s residence for help. The photograph of Qutubuddin Ansari begging for his life epitomises the plight of an entire community in Gujarat; thankfully, Ansari survived.
Flash points The Dec 6, 1992, Babri Masjid demolition; Sabarmati’s burning coach
The 2002 Gujarat riots also marked the coming of age of anti-communal activism. Several citizens, activists and lawyers who live within Gujarat have consistently fought against a state administration determined to block any probe. On the national stage, individuals like Teesta Setalvad have never relented, losing one legal battle to come back with another. Although Modi has been able to stay one step ahead of the legal snare, he is certainly bogged down by it. Outside Gujarat, he may have appeal for the BJP cadre, but regional parties want to keep a distance from him. If the big players of any regional front in the future are to be Mamata Banerjee, Naveen Patnaik and Nitish Kumar, the CMs of Bengal, Orissa and Bihar would not like to share a platform with Modi even if realpolitik were to force any sort of arrangement with the BJP. Indeed, one can argue that the political price of riots is now too high. Modi is quite stuck.
The perpetrators of riots are long-term players in the political landscape. The Thackerays have again bounced back in the local polls in Maharashtra. But the city of Mumbai has changed under their watch. The ferocity and cruelty of the violence that ripped right through Bombay (which became Mumbai later) in the aftermath of the Babri Masjid demolition, in two phases in December 1992 and January 1993, came to symbolise the worst face of a seemingly inclusive city. Till then the city would be described as a cosmopolitan megacity where caste, class and religion were not the dominant markers of public life. Bombay was the city of dreams, its streets offered anonymity, its pavements could turn into homes, its constant whirring machine of enterprise and entrepreneurship played the great equaliser. Surely, such a place could not be derailed by communal violence? This belief turned into a shattered myth in those two spans of ’92-93 when nearly 850 people were killed, 575 of them Muslims; over 2,000 injured and nearly 1,00,000 displaced.
After that, Bombay became Mumbai and no one really calls it a cosmopolitan place any longer. Resilient, yes, but not cosmopolitan. Bombay had its Hindu- and Muslim-dominated neighbourhoods but they were not community-insulated as has happened in the post-riots era. The ghettoising effect of 1993, which continues even today, has made the divisions sharper. In fact, it’s easier now to target this or that community and in many areas the “other” is not welcome at all, says Farooq Mapkar, who was witness to five namazis being shot in Hari Masjid by policemen, was wrongly accused of rioting and acquitted after 16 long years. A bank employee now, he says, “There is now a Muslim Mumbai and a Hindu Mumbai.”
Aligarh, 1990 125-150 people died in riots set off by killing of Muslims near a mosque by PAC. Misreporting, rumours, partisan PAC kept flames alive for nine days. (Photograph by HT (From Outlook, March 05, 2011)
The Shiv Sena in 1993 called itself the “defender of Hindus”. The Srikrishna Commission report famously indicted Shiv Sena chief Bal Thackeray and said that “like a veteran general, he commanded his loyal Shiv Sainiks to retaliate by organised attacks against Muslims, especially in January 1993”. The Mumbai police registered four offences against him for a communally provocative editorial exhorting such violence, but the go-ahead to prosecute was not given by the state government; then CM Sudhakarrao Naik famously said if certain leaders were arrested, Bombay would burn; it escaped his notice that the city had already burnt.
***
Riot After Riot
Fifty-eight major communal riots in 47 places since 1967
Ten in South India, 12 in East, 16 in West, 20 in North India
Ahmedabad has seen five major riots; Hyderabad, four; Calcutta, none since ’64*
The 1990s saw the most riots in the last five decades: 23
The 1970s saw seven riots, the ’80s, 14; the 2000s have seen 13
Total toll: 12,828 (South 597, West 3,426, East 3,581, North 5,224).
* In ’64, a wave of rioting in Calcutta, Jamshedpur and Rourkela killed 2,500.
Note: Only riots with a toll of five or more included; deaths due to bomb blasts not included
Data: Alka Gupta
***
Year Place Toll
Aug ’67 Hatia, Ranchi 183
Mar ’68 Karimganj, Assam 82
Sep ’69 Ahmedabad 512
May ’70 Bhiwandi, Mah. 76
May ’70 Jalgaon, Mah. 100
Oct ’77 Varanasi 5
Mar ’78 Sambhal, UP 25
Sep ’78 Hyderabad 20
Oct ’78 Aligarh 30
April ’79 Jamshedpur 120
Aug ’80 Moradabad 1,500
Apr ’81 Biharsharif 80
Sep ’82 Meerut 12
Dec ’82 Baroda 17
Feb ’83 Nellie, Assam 1,819
Sep ’83 Hyderabad 45
May ’84 Bhiwandi, Mah 146
Oct ’84 Delhi 2,733
Apr ’85 Ahmedabad 300
Jul ’86 Ahmedabad 59
Apr/May’87 Meerut 70
Mar ’89 Bhadrak, Orissa 17
Oct ’89 Indore 27
Oct ’89 Bhagalpur 1,161
Oct ’90 Ahmedabad 41
Oct ’90 Jaipur 52
Oct ’90 Jodhpur 20
Oct ’90 Lucknow 33
Oct ’90 Chandni Chowk, Delhi 100
Oct ’90 Hailakandi, Assam 37
Oct ’90 Patna 18
Oct ’90 Hyderabad 165
Nov ’90 Agra 31
Dec ’90 Hassan, Mandya, Mysore 60
Dec ’90 Hyderabad 200
Dec ’90 Aligarh 150
May ’91 Baroda 28
May ’91 Meerut 40
Oct ’92 Sitamarhi, Bihar 44
Dec ’92 Surat 152
Dec ’92 Malpura, Andhra 24
Dec ’92 Kanpur 254
Dec ’92 Bhopal 143
Dec ’92/Jan ’93 Bombay 872
Nov/Dec ’97 Coimbatore 20
Feb ’98 Coimbatore 60
Dec ’98 Surathkal, Karnataka 12
Mar 2001 Nalanda, Bihar 8
Mar ’01 Kanpur 14
Oct ’01 Malegaon 13
Feb-May ’02 Gujarat 1,267
May ’02 Marad, Kerala 9
Apr ’06 Aligarh 6
May ’06 Baroda 6
Dec ’07 Kandhamal 12
Oct ’08 Bhainsa, Andhra 6
Sep ’09 Miraj, Karnataka 5
Sep ’11 Bharatpur 10
Till ’92-93, the city police was seen as a proud force in khaki, worthy of being compared to Scotland Yard; their brutality and vehemence during the ’92-93 carnage turned them in the public eye into a force that did not hesitate to display the saffron beneath the khaki. As police officers and constables told the Indian People’s Tribunal in the immediate months, they “were Shiv Sainiks at heart and policemen of a supposedly secular state by accident”. As many as 32 policemen, including then joint commissioner R.D. Tyagi, were severely indicted by the Srikrishna Commission (SKC) for acts of omission and commission during the riots. None was punished; in fact, Tyagi was promoted to the post of city commissioner during the Sena-BJP regime in Maharashtra soon after.
Senior Sena leaders refuse to discuss the riots but point to the “thousands of illegal Bangladeshi migrants and Pakistani sympathisers” who live in the myriad lanes of the metropolis and “sometimes need to be put in their place”. If at that time the Muslims were the target, today the “other” is the bhaiyya or migrant from Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
Though political organisations may have found it increasingly difficult to stoke such large-scale, mind-numbing violence in recent years, Mumbai is still a tinderbox and vested interests can still play with people. Besides, the question of justice can’t be forgotten when we talk of riots. It rankles the victims that justice has still not been done; not only is justice a prerequisite for reconciliation, it’s also a necessary signal to those who believe they stand to gain by engineering such violence, victims say. The bomb blasts that followed in March 1993, killing 257 and injuring 800, have resulted in convictions, but no one has been punished for the ’92-93 riots except former Sena MLA Madhukar Sarpotdar who was convicted in July 2008 and let off on a Rs 5,000 bail. When the Shiv Sena-BJP came to power in Maharashtra in 1994, barely a year after Bombay burned, the administration withdrew as many as 3,000 cases registered against their workers. The subsequent Congress governments did not drop cases against Muslims that even the SKC concluded were false.
This one-sided justice has exacted its price. The Muslims in the ghettos are angry and often justifiably so. Every bomb blast and terror attack since has meant comb-and-search-and-arrest operations in their mohallas. Now after every major and minor terror attack on Mumbai, mohalla committees mobilise their peace soldiers in bastis, community elders come out requesting calm and peace, Muslims display their patriotism through solidarity marches in case they’re perceived as anti-nationals. The peace is kept but the tensions simmer.
Still, the cycle has been broken in other cities. Hyderabad, for instance, has moved on. The old city is still a hothouse, but communal violence no longer pays. Amir Ali of the influential Urdu daily, Siasat, recounts this brief history of his city’s riots. Before 1994, he says, violence took place every year over processions of Ganesh Chaturthi, Moharram or Bonalu (an Andhra festival). The violence stopped in 1994, when the TDP came to power, though one could not pinpoint an exact reason. Then, in 1998, a poster appeared in the old city of Hyderabad depicting Ganesh with Kaaba under one foot and Medina under the other. Police investigations revealed that the poster was the handiwork of a Hindu politician and former mayor of Hyderabad. He was in fact a member of the Majlise-e-Ittehadul-Muslimeen run by the Owaisi family that still has a grip on sections in the city! The linkages are circuitous, to say the least.
What this story illustrates is that an attempt to trigger a riot is a political tactic. Paul R. Brass, author and political scientist from the University of Washington, who’s studied India’s communal tension and violence, calls it the institutionalised riot system or IRS. This IRS, he says, was created largely in northern and western India and it can be activated by politicians during political mobilisation or elections, and “the production of a riot involves calculated and deliberate actions by key individuals, like recruitment of participants, provocative activities and conveying of messages, spreading of rumours”. There are frequent rehearsals until the time is ripe and the context is felicitous and there are no serious obstructions in carrying out the performance. Does such an IRS still prevail in Mumbai, or Bhiwandi, Malegaon, Aurangabad, Nashik, Moradabad, Ahmedabad?
Recently, activists of the Hindu right were arrested in Karnataka trying to raise a Pakistan flag in a Muslim area. They presumably hoped they would trigger a riot and blame it on Muslims. One must conclude that small riots can and in all likelihood may continue to happen (there was recently a Gujjar-Muslim clash in Mewat not far from Delhi), but it would take a certain conjunction of politics, intent and regime to trigger anything on the scale of the Gujarat riots.
Meanwhile, the political saga of Modi continues, with his national ambitions all too obvious. As things stand now, he can be a national player only if the BJP gets a majority on its own. As that currently seems unlikely, Modi can perhaps examine his predicament from a philosophical, moral or literary viewpoint. He could ruminate over that quote of Lady Macbeth’s who kept washing her hands. “Out, damn’d spot! out, I say”!
Riot Triggers
Social: The feeling of being left out of the discourse. Especially prevalent among minorities who are excluded, deliberately or otherwise, from mainstream events and activities, leading to ghettoisation.
Economic: The feeling of being left behind. Poor education, unemployment lead to marginalisation of the have-nots. Heightened by sense of deprivation and sight of conspicuous consumption.
Political: Parties and politicians play on the emotions of votebanks, often to expand it, by mobilising mobs and whipping up passions and fears over illegal immigration and demographic change
Administrative: The feeling of being targeted and/or ignored by the immediate touchpoints of government—the police and civic administration. Denial of rights and harassment spawn sense of injustice.
Religious: Perceived slights to sentiments. Can be sparked by a procession in a ‘sensitive’ area; a loud prayer, a road blocked for prayers, or an animal’s carcass thrown into a place of worship
Commercial: Rivalries sparked off by encroachment of traditional areas of business and economic activity
Verbal: Provocative speeches that stereotype and instigate the intended target on the basis of language, religion and sexual habits. Rabble-rousing about ‘appeasement’. Sporting events as a test of patriotism and nationalism.
Global: Rumours and whispers that travel across the wired world about defacement or denigration of holy scriptures and holy figures in books, movies, newspaper articles, posters, cartoons.
***
By Saba Naqvi in New Delhi and Smruti Koppikar in Mumbai
skip to main |
skip to sidebar

Communalism all day everyday (hk 2015)


extract from a photo on street

Seeds of Hate - Picture of Bricks collected by the Hindu right Ram Janmabhoomi movement (Photo PTI)
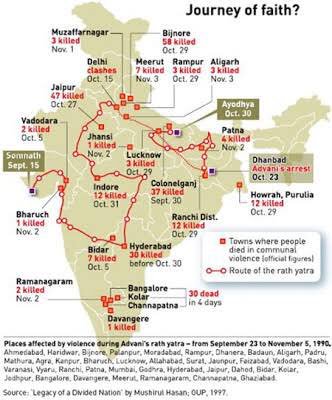
Journey of Faith? - Places affected by violence during BJP's Rath Yatra
Resources for all concerned with culture of authoritarianism in society, banalisation of communalism, (also chauvinism, parochialism and identity politics) rise of the far right in India (and with occasional information on other countries of South Asia and beyond)
Subscribe via email
see Comunalism Watch on mobile phones
Archive
Links
- Fast Track To Troubling Times: 100 Days of Narendra Modi – A Counter Report
- Hindu Nationalism in the United States: A Report on Nonprofit Groups
- Gujarat Carnage 2001-2010
- Communalism Combat
- Anhad
- Sahmat News
- Plural India
- Citizens For Justice and Peace
- Coalition Against Communalism
- For Defence of Teesta Setalvad
- Secular Democracy
- Citizens For Peace
- South Asia Citizens Web
- Truth of Gujarat
- Desh Kosh
- Feku
- Vision Jafri
- Narendra Modi Facts
- Orissa Burning: The anti christian pogrom of Aug-Sep 2008
- Remembering 1992
- Thus Spake Srikrishna
- Janta Ka Aina
- Onlinevolunteers org
- Campaign to Stop Funding Hate
- Awaaz South Asia
- Coalition Against Genocide
- Sangh Samachar
- Stop The Hatred
- Barbarta Kay Virudh: An anti fascist blog in Hindi
- The Pink Chaddi Campaign
- Ban Vishwa Hindu Parishad
- Report of Indian People's Tribunal on Communalism in Orissa
- The Truth on Gujarat 2002 - A Tehelka investigation
- Communalism and Religious Fundamentalism in India: A Resource File [A PDF file]
- Secularism is a women's issue
- Centre for Secular Space
- Human Rights for All
- Gulail
- Holy Cow & Other Bull
- Searchlight Magazine
- Anti Fascist Network
- Ras l'front
Pages
Tags / Keywords
Translate
Feed from Dilip Simeon's blog
Communalism all day everyday

Communalism all day everyday (hk 2015)
See Therapist for "Hurt Sentiments"
Freedom from Hindutva
extract from a photo on street

Seeds of Hate - Picture of Bricks collected by the Hindu right Ram Janmabhoomi movement (Photo PTI)
Map of L K Advani's Rath Yatra of 1990

Journey of Faith? - Places affected by violence during BJP's Rath Yatra
About Us / Disclaimer
This is a collaborative space run by an informal collective of people from across India and elsewhere. The blog was started many years ago under the aegis of South Asia Citizens Web. All web content placed here is done in public interest; it may be freely used by people for non commercial purposes. Please remember to give credit to original copyrighted sources and seek permission for further use.
Disclaimer: Posting of content here does not constitute endorsement by the Communalism Watch Cooperative.
Disclaimer: Posting of content here does not constitute endorsement by the Communalism Watch Cooperative.