[by] Rakhi Chakrabarty | Jan 13, 2014, 12.06 AM IST (The Times of India)
As fog and dusk enveloped Muzaffarnagar's Loi village, riot victims huddled in their cramped tents - a fragile refuge after rioters destroyed their ancestral homes in September. Mothers clung to their babies, striving to protect them from the bitter winter chill. Hungry children cried for food as women struggled to make rotis on a chullah fired by dry sugarcane leaves.
About 50 yards away, stood a couple of monstrous excavators - the most visible sign of the state in riot-ravaged Muzaffarnagar. While the world celebrated New Year, these excavators had rolled into Loi and demolished shelters of about 3,600 riot victims.
While tracking the communal riots that singed Muzaffarnagar and neighbouring Shamli, it has increasingly become clear that the Uttar Pradesh government has abdicated its responsibility and let wounds fester. First it failed to save lives and property in one of the most vicious riots in recent times. Then, it failed to assuage the pain of riot victims by not providing adequate relief and compensation. The government's supply of ration, medicines and doctors, milk for babies, clothes and blankets for riot victims has been intermittent and hugely inadequate. And when the Sup-reme Court rapped it for suffering and deaths in the relief camps, the UP government responded with a drive to dismantle most of the 58 camps.
By Muzaffarnagar district magistrate Kaushal Raj Sharma's estimate, the riots displaced 51,000 people - 27,198 from Muzaffarnagar and the rest from Shamli - from 150 villages. Four months after the riots, only 950 families from nine ''severely affected'' villages have received Rs 5 lakh compensation from the state government. Yardstick for picking only nine villages is not clear. Fate of the other homeless riot victims is uncertain.
The government has also failed to remove fear - many riot accused still roam freely - and restore confidence so that victims return home. Instead, Samajwadi Party's government forced many of them to sign affidavits pledging never to return to their ancestral villages if they accepted the Rs 5 lakh compensation. This move deliberately or otherwise has heightened a sense of hurt and injustice. It could deepen the communal divide.
Other mainstream political parties too have been scarce in their solidarity with or relief for riot victims. There is scant investment in confidence building between the warring communities. The vacuum left by political parties and civil society groups in this rural belt of western UP has been filled in by religious outfits. A slew of Muslim religious organizations have been helping with a steady supply of relief and even mass marriage of daughters of riot victims. They are also building houses and helping riot victims, who lost their livelihood, earn.
A fact-finding team of intellectuals from Delhi University and JNU found that the UP government has outsourced relief work to religious outfits. A reality check at ground zero lends credence to this finding and bares an insidious design as old as the idea of India, but not yet rusty. Politics perilously continues to stir the religious-emotional cauldron, either to consolidate electoral power in our ballot box democracy or to save an eroding political base.
Muzaffarnagar has a notorious crime record, but its communal amity stood out in UP.
In the Jatland, Muslims and Hindus have lived in harmony for centuries. It remained mostly unscathed in the communal frenzy over Partition or Babri masjid demolition.
Village communities built over the ages included people from all backgrounds contributing to the rural economy. Muslim farm labourers worked on land owned by Jats, artisans - blacksmiths, carpenters - were settled by landlords regardless of their religious identity to make the village self-sufficient.
Economy and not religion was the overriding factor. Every member preserved his religious or social identity while being part of a cohesive whole. The September 2013 riots changed that, rupturing social relations cemented over centuries. This is bound to tell on the economy of the country's sugar bowl.
Demography of the region is poised for a change too. Villages here had a largely mixed population. The riots drove out mostly Muslims. A large section of them refuse to return ever. The pattern of settlement of riot victims, mostly with help from religious outfits, portends ghettoisation. Communal homogeneity is inimical to a secular democracy like India. But this could be the future for post-riot villages, churned by a blend of religious segregation and political opportunism.
Help in adversity strengthens bonds and extracts loyalty. During the riots, community leaders and village pradhans - both Hindus and Muslims - emerged as saviours and guardians. If Muslim riot victims are beholden to their community leaders for standing by in crisis, Hindu villagers commend theirs for pandering to the majority's victimhood - lurking in their collective subconscious.
These pradhans and community leaders are potential ghetto overlords. After all amidst UP's political ferment, ghettos could well become the newest captive vote banks controlled by ghetto overlords. They would be open to exploitation by political parties - at a price - for gains in elections.
History, as Stephen Chan says, shows that reconciliation is difficult in a polarized society till each pole lives out its subjectivity. Without reconciliation, the future does not augur peace. Muzaffarnagar's communal frisson spells the end of certainty, at least for now.
Source: http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/home/opinion/edit-page/How-ghettos-get-made-Its-dangerous-that-Akhileshs-government-has-outsourced-riot-relief-work-to-religious-outfits/articleshow/28713529.cms
skip to main |
skip to sidebar

Communalism all day everyday (hk 2015)


extract from a photo on street

Seeds of Hate - Picture of Bricks collected by the Hindu right Ram Janmabhoomi movement (Photo PTI)
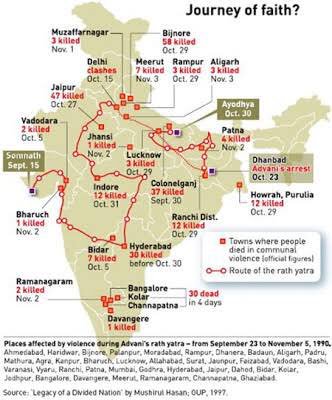
Journey of Faith? - Places affected by violence during BJP's Rath Yatra
Resources for all concerned with culture of authoritarianism in society, banalisation of communalism, (also chauvinism, parochialism and identity politics) rise of the far right in India (and with occasional information on other countries of South Asia and beyond)
Subscribe via email
see Comunalism Watch on mobile phones
Archive
Links
- Fast Track To Troubling Times: 100 Days of Narendra Modi – A Counter Report
- Hindu Nationalism in the United States: A Report on Nonprofit Groups
- Gujarat Carnage 2001-2010
- Communalism Combat
- Anhad
- Sahmat News
- Plural India
- Citizens For Justice and Peace
- Coalition Against Communalism
- For Defence of Teesta Setalvad
- Secular Democracy
- Citizens For Peace
- South Asia Citizens Web
- Truth of Gujarat
- Desh Kosh
- Feku
- Vision Jafri
- Narendra Modi Facts
- Orissa Burning: The anti christian pogrom of Aug-Sep 2008
- Remembering 1992
- Thus Spake Srikrishna
- Janta Ka Aina
- Onlinevolunteers org
- Campaign to Stop Funding Hate
- Awaaz South Asia
- Coalition Against Genocide
- Sangh Samachar
- Stop The Hatred
- Barbarta Kay Virudh: An anti fascist blog in Hindi
- The Pink Chaddi Campaign
- Ban Vishwa Hindu Parishad
- Report of Indian People's Tribunal on Communalism in Orissa
- The Truth on Gujarat 2002 - A Tehelka investigation
- Communalism and Religious Fundamentalism in India: A Resource File [A PDF file]
- Secularism is a women's issue
- Centre for Secular Space
- Human Rights for All
- Gulail
- Holy Cow & Other Bull
- Searchlight Magazine
- Anti Fascist Network
- Ras l'front
Pages
Tags / Keywords
Translate
Feed from Dilip Simeon's blog
Communalism all day everyday

Communalism all day everyday (hk 2015)
See Therapist for "Hurt Sentiments"
Freedom from Hindutva
extract from a photo on street

Seeds of Hate - Picture of Bricks collected by the Hindu right Ram Janmabhoomi movement (Photo PTI)
Map of L K Advani's Rath Yatra of 1990

Journey of Faith? - Places affected by violence during BJP's Rath Yatra
About Us / Disclaimer
This is a collaborative space run by an informal collective of people from across India and elsewhere. The blog was started many years ago under the aegis of South Asia Citizens Web. All web content placed here is done in public interest; it may be freely used by people for non commercial purposes. Please remember to give credit to original copyrighted sources and seek permission for further use.
Disclaimer: Posting of content here does not constitute endorsement by the Communalism Watch Cooperative.
Disclaimer: Posting of content here does not constitute endorsement by the Communalism Watch Cooperative.